10 Groundbreaking Scientific Discoveries of 2017
February 1, 2018
2017 may have been a wild ride, but whether it personally was a great year or a terrible one, tons of groundbreaking, interesting, and flat out weird discoveries were made in the scientific community. Here’s a list of just a few of the myriad of diverse findings.

Yet another part of Einstein’s famous theory of general relativity has been proven to exist. Gravitational waves are ripples in the very fabric of spacetime caused by objects moving through space -the more massive the object, the greater the gravitational waves. The initial measurement was detected in 2015 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, but wasn’t announced to the public until early 2017. The origin of the waves were two black holes about 30 times the mass of our Sun, some 1.3 billion light years away from Earth. After over a year of checking over their measurements to make sure that their discovery wasn’t simply a glitch in their system, we finally have even more evidence to back theoretical physicist Albert Einstein.
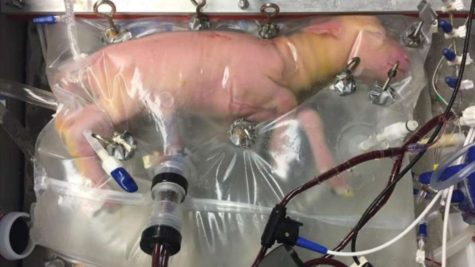
Premature lambs were able to be sustained outside of their mothers’ wombs in plastic bags. By mimicking the same environment that would be found inside of a healthy sheep, the premature lambs were able to survive for 4 weeks, even growing wool, developing organs, and opening their eyes for the first time in these bags. This gives hope for the future of premature human babies. Scientists are hoping that one day, similar bags will be able to allow a premature baby to finish out it’s gestation, thus decreasing infant mortality rates.

Only 39.5 light years away, in the Aquarius constellation, the ultracool dwarf star, Trappist-1, was found to have 4 more potentially habitable planets than previously thought, bringing the grand total to a mind blowing seven planets. Astronomers used transit photometry, a method that measures the dips in light that occur when a planet passes in between the star and Earth. Each of these seven planets are in Trappist-1’s “habitable zone”, or the area in any given solar system where liquid water could potentially exist. Though there has not been enough data to suggest that these planets are, in fact, harboring life, these planets are waiting to be occupied.

Artificial intelligence, for the first time ever, beat world champion, Ke Jie, in the ancient Chinese board game of “Go” all on it’s own. AlphaGo Zero is an artificial intelligence that uses algorithms to calculate and come up with solutions to any problem it is given. While there were three other iterations of AlphaGo before Zero came along, AlphaGo Zero is special because it learned how to play this game without being fed human data. Essentially, the artificial intelligence taught itself better strategies by playing 4.9 million games of “Go” against itself, coming up with novel strategies that humans have yet to come up with in a matter of days. The possible scientific implications of this are huge, namely in calculating ways to fold proteins to come up with better and more effective drugs.

SpaceX, a private space exploration company founded by Tesla motors creator Elon Musk, made and successfully launched and relaunched a rocket strong enough to send supplies into orbit. Less than a year after the initial launch into space, the rocket was strapped with a satellite and sent off, once more making SpaceX the first company to ever reuse an orbital strength rocket. Needless to say, building a rocket and subsequently sending it to space is expensive. By having a reusable rocket, this could potentially bring down the cost of bringing supplies to space tenfold. While the rocket landed safely after it’s second mission, there are plans for there to be a third.

After the merging of two super dense neutron stars, scientists were able to put together a model that reveals the mysterious origins of heavy metals in our, universe, precisely gold. In the event of a neutron star merger, there exists a giant radioactive fireball. Within these giant collisions, there is enough energy for lighter elements to fuse and create the heavier elements that are ejected into space in the aftermath. This solved the mystery of where much of the gold and other heavy elements that has been measured in our universe came from. While supernovas could account for some of it, this makes up for what was previously a mystery.

Ceres, a dwarf planet within our own solar system, was found to have organic molecules on its surface. A decade after its launch in 2007, the Dawn mission announced these findings in a scientific journal in early February of 2017. These building blocks are long chains of carbons that make up carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and most importantly, nucleic acids, the precursor to RNA and DNA. These organic molecules are also likely to be native to the rocky body. This becomes increasingly exciting when taking into account the fact that Ceres is thought to have a subsurface ocean warmed by its core making it an unlikely contender in the search for extraterrestrial life.
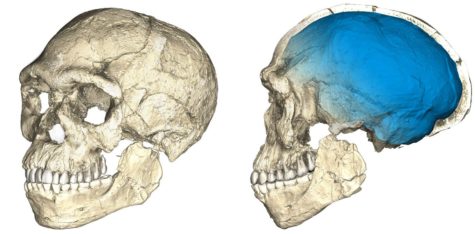
Modern humans (Homosapiens) were thought to have first appeared some 200,000 years ago in Africa before spreading out and populating other parts of the world alongside other, now extinct, species of humans. This long believed idea, however, has been challenged after scientists found, among tools and small animal bones, five Homo-sapien specimens, in a quarry in northwestern Africa. While originally dated to only be about 40,000 years old, newer, more accurate forms of dating suggested that the bones were actually 300,000 years old! Not only does this mean that paleoanthropologists (scientists that study human evolution) will need to scrap models of ancient history, it also shows that Homo-sapiens had a much larger geographical range than ever.

